What is a blood clot?
A blood clot is a clump of blood that has changed from a liquid to a gel-like or semisolid state. Clotting is a necessary process that can prevent you from losing too much blood in certain instances, such as when you’re injured or cut.
When a clot forms inside one of your veins, it won’t always dissolve on its own. This can be a very dangerous and even life-threatening situation.
An immobile blood clot generally won’t harm you, but there’s a chance that it could move and become dangerous. If a blood clot breaks free and travels through your veins to your heart and lungs, it can get stuck and prevent blood flow. This is a medical emergency.
You should call your doctor immediately if you think you might have a blood clot. A healthcare professional will be able to look at your symptoms and medical history and let you know what steps to take from there.
Types of blood clots
Your circulatory system is made up of vessels called veins and arteries, which transport blood throughout your body. Blood clots can form in veins or arteries.
When a blood clot occurs in an artery, it’s called an arterial clot. This type of clot causes symptoms immediately and requires emergency treatment. The symptoms of an arterial clot include severe pain, paralysis of parts of the body, or both. It can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
A blood clot that occurs in a vein is called a venous clot. These types of clots may build up more slowly over time, but they can still be life-threatening. The most serious type of venous clot is called deep vein thrombosis.
Deep vein thrombosis
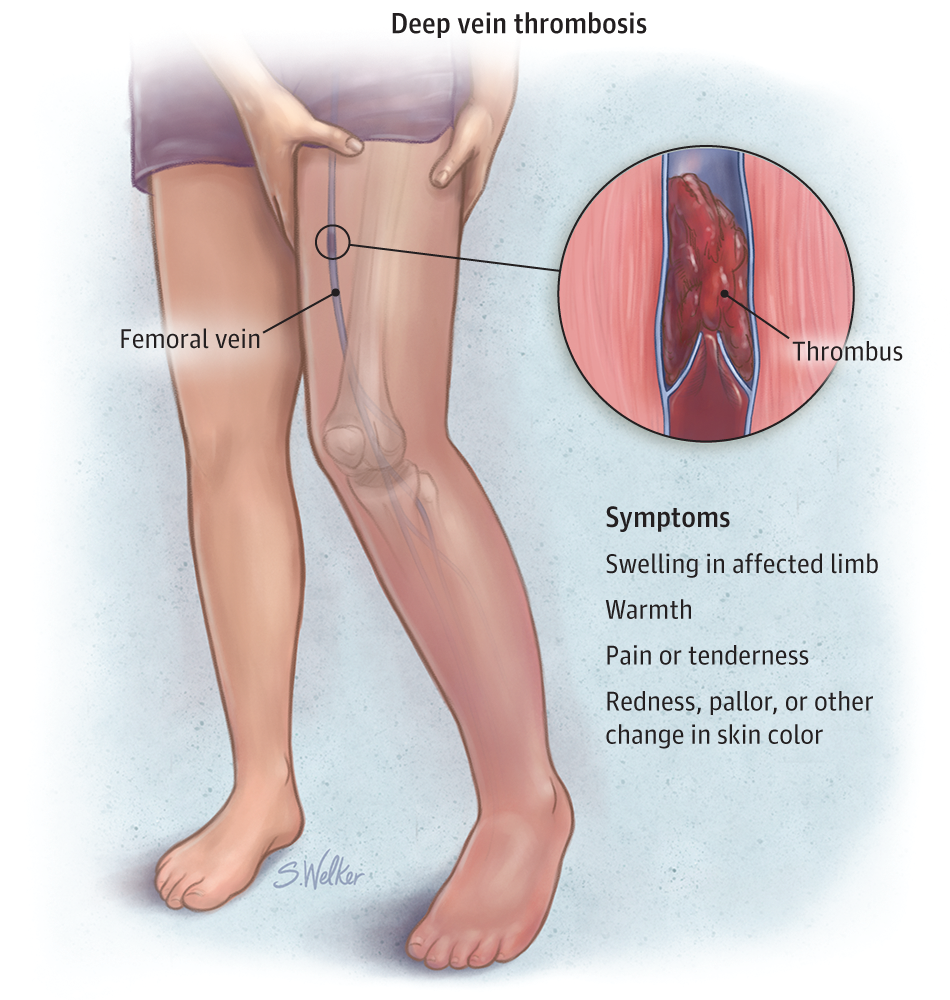
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is the name for when a clot forms in one of the major veins deep inside your body. It’s most common for this to happen in one of your legs, but it can also happen in your arms, pelvis, lungs, or even your brain.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)Trusted Source estimates that DVT, together with pulmonary embolism (a type of venous clot affecting the lungs) affects up to 900,000 Americans each year. These types of blood clots kill approximately 100,000 Americans annually.
There’s no way to know whether you have a blood clot without medical guidance. If you know the most common symptoms and risk factors, you can give yourself the best shot at knowing when to seek an expert option.
It’s possible to have a blood clot with no obvious symptoms. When symptoms do appear, some of them are the same as the symptoms of other diseases. Here are the early warning signs and symptoms of a blood clot in the leg or arm, heart, abdomen, brain, and lungs.
Blood clot in the leg or arm

The most common place for a blood clot to occur is in your lower leg, says Akram Alashari, MD, a trauma surgeon and critical care physician at Grand Strand Regional Medical Center.
A blood clot in your leg or arm can have various symptoms, including:
- swelling
- pain
- tenderness
- a warm sensation
- reddish discoloration
Your symptoms will depend on the size of the clot. That’s why you might not have any symptoms, or you might only have minor calf swelling without a lot of pain. If the clot is large, your entire leg could become swollen with extensive pain.
It’s not common to have blood clots in both legs or arms at the same time. Your chances of having a blood clot increase if your symptoms are isolated to one leg or one arm.
Blood clot in the heart, or heart attack

A blood clot in the heart causes a heart attack. The heart is a less common location for a blood clot, but it can still happen. A blood clot in the heart could cause your chest to hurt or feel heavy. Lightheadedness and shortness of breath are other potential symptoms.
Blood clot in the abdomen

Severe abdominal pain and swelling could be symptoms of a blood clot somewhere in your abdomen. These could also be symptoms of a stomach virus or food poisoning.
Blood clot in the brain, or stroke
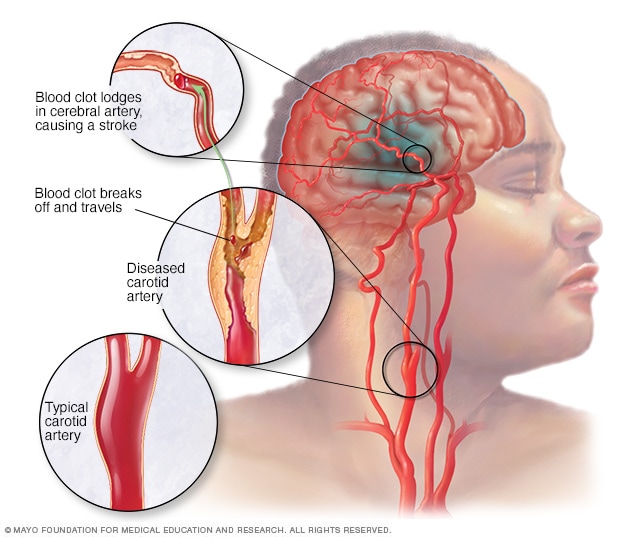
A blood clot in the brain is also known as a stroke. A blood clot in your brain could cause a sudden and severe headache, along with some other symptoms, including sudden difficulty speaking or seeing.
Blood clot in the lungs, or pulmonary embolism

A blood clot that travels to your lungs is called a pulmonary embolism (PE). Symptoms that could be a sign of a PE are:
- sudden shortness of breath that isn’t caused by exercise
- chest pain
- palpitations, or rapid heart rate
- breathing problems
- coughing up blood
What are the risk factors?
Certain risk factors increase your chances of having a blood clot. A recent hospital stay, especially one that’s lengthy or related to a major surgery, increases your risk of a blood clot.
Common factors that can put you at a moderate risk for a blood clot include:
- age, especially if you’re over 65 years old
- lengthy travel, such as any trips that caused you to sit for more than four hours at a time
- bed rest or being sedentary for long periods of time
- obesity
- pregnancy
- a family history of blood clots
- smoking
- cancer
- certain birth control pills
When to call a doctor
Diagnosing a blood clot by symptoms alone is very difficult. According to the CDC, almost 50 percent of people with DVT have no symptoms. That’s why it’s best to call your doctor if you think that you might have one.
Symptoms that come out of nowhere are especially concerning. Call your local emergency services immediately if you experience any of the following:
- sudden shortness of breath
- chest pressure
- difficulty breathing, seeing, or speaking
Your doctor or other healthcare professional will be able to tell whether there’s reason for concern and can send you for more tests to determine the exact cause. In many cases, the first step will be a noninvasive ultrasound. This test will show an image of your veins or arteries, which can help your doctor make a diagnosis.
Symptoms of a blood clot
Symptoms vary depending on where in your body the clot is. These include:
| Arm or leg | Brain | Heart | Abdomen | Lung |
| • swelling • soreness • sudden pains • warmth in one spot |
• changes in vision • seizures • speech impairment • weakness • changes in sensation in the face, one arm or leg, or one side of your body |
• shortness of breath • excessive sweating • chest pains that may extend down the left arm • nausea • dizziness • passing out |
• serious abdominal pain • diarrhea • vomiting • blood in the vomitus or stool |
• sharp chest pains • a cough with blood • sweating • difficulty breathing • fever • a rapid pulse • dizziness • passing out |
Who is at risk?
You may be at risk for forming a blood clot if you:
- are obese
- are a smoker
- are over the age of 60
- take oral contraceptives
- have a chronic inflammatory disease
- have atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation
- have congestive heart failure
- have cirrhosis
- have cancer
- have fractures in your extremities, especially the lower extremities or pelvis
- are pregnant
- have a family history of clotting disorders
- are unable to walk
- sit for long periods of time
- travel frequently
How to prevent blood clots
Blood clots can be treated with blood thinning medications. But it’s better to take steps to prevent blood clots from forming because complications can be serious and even fatal if not diagnosed early.
Work to control your risk factors so you can reduce your chances of developing a blood clot. Consider taking the following steps:
- lose weight if you are obese.
- stop smoking.
- tell your doctor about any family history of blood clotting.
It’s important to get treatment and follow your doctor’s instructions for lowering your risk factors. Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet high in omega-3 rich foods, fruits and vegetables, and foods rich in vitamin E may also help.
Be physically active. Immobility is a major factor that can lead to clots forming, especially in the legs. Make a point to get up regularly and walk around if you sit for long periods at a desk or if you travel frequently.
Be aware of any other conditions that may increase your risk for a blood clot, and talk to your doctor about strategies to reduce your risk.
PRODUCTS TO PREVENT BLOOD CLOTS NATURALLY WITH NO SIDE EFFECTS
Remember that good health start from good nutrition There’s nothing more important than our good health. That’s our principal capital asset.
Our natural and organic products are made from the finest ingredient, grown, and collected from the best source and produce with the most advanced technology.
Our natural and organic products are design to tackle the root cause of the problem and treat it naturally with no side effects.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE THIS TOO